lua
基本操作
2021-11-01 09:51:12
类型
数字取整操作
使用计算方式
使用%运算符,得到的结果是数字。x%1表示x的小数部分,x-x%1表示x的整数部分。使用函数库
math.ceil()
math.ceil(12.2) --返回13
math.ceil(12.7) --返回13
math.ceil(12.0) --返回12
a, b = math.modf(23.67) -- a=23 b=67- 使用字符串格式化
得到的结果是字符串形式string.format(“%d”, 17.325) --输出17
字符串连接
> print("a" .. 'b')
ab
> print(157 .. 428)
157428
>使用 # 来计算字符串的长度
> len = "www.runoob.com"
> print(#len)
14
> print(#"www.runoob.com")
14
>表
-- 创建一个空的 table
local tbl1 = {}
-- 直接初始表
local tbl2 = {"apple", "pear", "orange", "grape"}遍历
local tbl = {"apple", "pear", "orange", "grape"}
for key, val in pairs(tbl) do
print("Key", key, 'value', val)
end输出
Key 1 value apple
Key 2 value pear Key 3 value orange
Key 4 value grape
判空
if next(a) ~= nil
--不是空表
else
--空表
end变量swap
x, y = y, x -- swap 'x' for 'y'
a[i], a[j] = a[j], a[i] -- swap 'a[i]' for 'a[j]'流程控制
Lua认为false和nil为假,true和非nil为真。
要注意的是Lua中 0 为 true
多返回值
> s, e = string.find('i have a word', 'word')
> print(s, e)
10 13可变参数
通常在遍历变长参数的时候只需要使用 {...},然而变长参数可能会包含一些 nil,那么就可以用 select 函数来访问变长参数了:select('#', ...) 或者 select(n, ...)
select('#', ...)返回可变参数的长度。select(n, ...)用于返回从起点 n 开始到结束位置的所有参数列表。
调用 select 时,必须传入一个固定实参 selector(选择开关) 和一系列变长参数。如果 selector 为数字 n,那么 select 返回参数列表中从索引 n 开始到结束位置的所有参数列表,否则只能为字符串 #,这样 select 返回变长参数的总数。
字符串
Lua 语言中字符串可以使用以下三种方式来表示:
- 单引号间的一串字符。
- 双引号间的一串字符。
[[与]]间的一串字符。
迭代器
- pairs: 迭代 table,可以遍历表中所有的 key 可以返回 nil
- ipairs: 迭代数组,不能返回 nil,如果遇到 nil 则退出
目前 研究进度
lua 深入
2022-07-22 11:39:11
热更新
lua 的栈与内存限制
- 一个lua文件不能超过 262144 个常量
- 一个控制结构不能超过 32895 个栈
- upvalue数量不能超过 60 个
- Lua 的每个函数(function)中不能超过 200 个本地变量
ELuna
绑定C++类
使用ELuna::registerClass( lua_State, className, constructor) 函数绑定一个C++类。第一个参数是lua_state, 第二个参数是类在Lua中的名字。第三个参数constructor是这个类要用到的构造函数,通过传递具体的ELuna::constructor 函数来为这个类设置好一个构造函数,这个函数模板参数中的第一个参数是构造函数所属的类,后面的参数为构造函数的参数类型列表。如你需要为类Test设置一个参数为int的构造函数,则须传递ELuna::constructor 到registerClass函数中,模板参数中的int就是这个类的构造函数所需的参数类型。在Lua中创建对象时需这样写: test = Test(1)。
绑定c++类成员函数
使用ELuna::registerMethod(lua_State, funcName, func) 函数绑定一个c++类成员函数。第一个参数同上面的函数。第二个参数是函数在Lua中的名字。第三个参数是这个函数的地址。如你要注册Test类的foo函数到Lua中,应利用ELuna::registerMethod(L,”foo”, &Test::foo)来注册函数。在Lua中的调用为test:foo()。
绑定c++函数
使用ELuna::registerFunction(lua_State, funcName, func)函数c++函数。这个函数中参数的意义同registerMethod函数。例如C++中有一函数foo,利ELuna:: registerFunction(L,“foo”, &foo)注册这个函数,在Lua调用为foo()。
绑定Lua函数
使用ELuna::LuaFunction类为Lua函数生成一个相应的C++中的对象,调用函数通过使用类的”()”方法来实现。比如在Lua中有一个函数foo(a),其中参数a是number型,且无返回值,则在C++中的绑定方法为先利用 ELuna::LuaFunction luaFoo(L, “foo”) 创建一个C++对象,其中模板参数是这个Lua函数的返回值类型,因为foo无返回值,所以为void,LuaFunction的第一个参数是lua_state,第二个参数是这个Lua函数的名字。在C++中的调用方式为luaFoo(1)。
绑定Lua中的Table类型
使用ELuna::LuaTable类生成一个Lua Table在c++中的对象,读取插入元素通过”get”, “set”方法。比如Lua中有一个Table变量luaTable = {“hello”},在C++中使用ELuna:: LuaTable luaTable(L, “luaTable”)来为luaTable在C++中生成一个对象,调用luaTable.get(1)来取得luaTable中key为1的字符串”hello”,其中模板参数char* 为get返回的value类型。调用luaTable.set(2, “world”)来为luaTable插入一个key=2,value=”world”的键值对。
示例
::: code-tabs#shell
@tab:active c++
#include <stdio.h>
#include "ELuna.h"
//define a class
class CPPClass
{
public:
CPPClass(const char* name): m_name(name){
printf("%s %p Constructor!\n", name, this);
}
~CPPClass(){
printf("%s %p Destructor!\n", m_name, this);
}
//define method
void cppPrint(const char* word) {
printf("%s: %s\n", m_name, word);
}
int cppSum(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
void print() {
printf("%s: %p\n", m_name, this);
}
CPPClass& createRef(CPPClass& p) {
printf("%s %s %p %p createRef!\n", m_name, p.m_name, &p, this);
p.m_name = "ref";
return p;
}
private:
const char* m_name;
};
//define function
void cppPrint(char* str) {
printf("cppPrint: %s\n", str);
}
int cppSum(int a, int b){
return a + b;
}
CPPClass* testnil(CPPClass* c)
{
printf("CPPClass c: %p\n", c);
return nullptr;
}
void testCPP(lua_State* L) {
//register a class and it's constructor. indicate all constructor's param type
ELuna::registerClass<CPPClass>(L, "CPPClass", ELuna::constructor<CPPClass, const char* >);
//register a method
ELuna::registerMethod<CPPClass>(L, "cppPrint", &CPPClass::cppPrint);
ELuna::registerMethod<CPPClass>(L, "cppSum", &CPPClass::cppSum);
ELuna::registerMethod<CPPClass, CPPClass&>(L, "createRef", &CPPClass::createRef);
ELuna::registerMethod<CPPClass>(L, "print", &CPPClass::print);
//register a function
ELuna::registerFunction(L, "cppPrint", cppPrint);
ELuna::registerFunction(L, "cppSum", cppSum);
ELuna::registerFunction(L, "testnil", testnil);
}
void testLua(lua_State* L) {
//new a LuaFunction object to bind lua function. indicate return value type
ELuna::LuaFunction<void> luaPrint(L, "luaPrint");
ELuna::LuaFunction<int> luaSum(L, "luaSum");
//run Luafunction's () to call lua function
luaPrint("hello world");
printf("luaSum: %d\n", luaSum(1,2));
//register a lua table
ELuna::LuaTable luaTable(L, "luaTable");
//set table's key and value
luaTable.set(2, "world");
printf("LuaTable: %s %s\n", luaTable.get<int, char*>(1), luaTable.get<int, char*>(2));
}
const char *fileName = "../sample/sample.lua";
int main()
{
lua_State *L = ELuna::openLua();
testCPP(L);
ELuna::doFile(L, fileName);
testLua(L);
ELuna::closeLua(L);
getchar();
return 0;
}@tab lua
--new a class
local cppClass = CPPClass("cppClass")
cppClass:print()
--call cpp method
cppClass:cppPrint("Hello world!")
print("CPPClass's cppSum:", cppClass:cppSum(1,2))
--call cpp function
cppPrint("Hello world!")
print("cppSum:", cppSum(1,2))
print("testnil: ", testnil(cppClass))
-- print("testnil: ", testnil(nil))
--define lua function
function luaPrint(str)
print("luaPrint:", str)
end
function luaSum(a, b)
return a + b
end
--define table
luaTable = {"hello"}
local refClass = cppClass:createRef(cppClass)
print("createRef: ", refClass, cppClass)
cppClass:print()
refClass:print():::
lua自动化测试指南
2021-11-24 11:15:22
luarocks安装过程
linux安装luarocks(RedHat系列)
To get a default installation of Lua and LuaRocks under /usr/local
First, ensure that you have development tools installed on your system, otherwise run the command below to install them
shellsudo yum install libtermcap-devel ncurses-devel libevent-devel readline-develbuild and install Lua, run the following commands to download the package tar ball, extract, build and install it.(lua source code)
shell-$ curl -R -O http://www.lua.org/ftp/lua-5.1.4.tar.gz -$ tar -zxf lua-5.1.4.tar.gz -$ cd lua-5.1.4 -$ make linux test -$ sudo make installDownload and unpack the LuaRocks tarball using following commands.
shell-$ wget https://luarocks.org/releases/luarocks-3.8.0.tar.gz -$ tar zxpf luarocks-3.8.0.tar.gz -$ cd luarocks-3.8.0Run
./configure --with-lua-include=/usr/local/include. (This will attempt to detect your installation of Lua. If you get any error messages, see the section "Customizing your settings", below.)Run
make.As superuser, run
make install.
linux安装luarocks(Debian系列)
To get a default installation of Lua and LuaRocks under /usr/local
First, ensure that you have development tools installed on your system, otherwise run the command below to install them
shell-$ sudo apt install build-essential libreadline-dev unzipbuild and install Lua, run the following commands to download the package tar ball, extract, build and install it.(lua source code)
shell-$ curl -R -O http://www.lua.org/ftp/lua-5.1.4.tar.gz -$ tar -zxf lua-5.1.4.tar.gz -$ cd lua-5.1.4 -$ make linux test -$ sudo make installDownload and unpack the LuaRocks tarball using following commands.
shell-$ wget https://luarocks.org/releases/luarocks-3.8.0.tar.gz -$ tar zxpf luarocks-3.8.0.tar.gz -$ cd luarocks-3.8.0Run
./configure --with-lua-include=/usr/local/include. (This will attempt to detect your installation of Lua. If you get any error messages, see the section "Customizing your settings", below.)Run
make.As superuser, run
make install.
windows子系统linux安装luarocks
- 安装gcc
- sudo apt install lua5.1
- sudo apt install luarocks
- sudo apt install lua-busted
- 安装pcre2,安装rapidjson(这两个可以直接copy dbproxy项目里的lua文件)
- 安装完成
windows安装luarocks (极其难用 不建议在Windows下操作)
安装完成后cmd运行
luarocks看是否安装成功找不到luarocks命令时,需要将图示四个文件copy放入
lua\5.1\路径下
安装busted
luarocks install busted* 如若出现Error: Parse error processing dependency 'lua_cliargs = 3.0',请键入where luarocks查看路径是否为您的安装路径,此现象为您在设备上安装了多个版本的luarocks系统无法确定安装版本。- 如若出现
'mingw32-gcc'不是内部或外部命令,也不是可运行的程序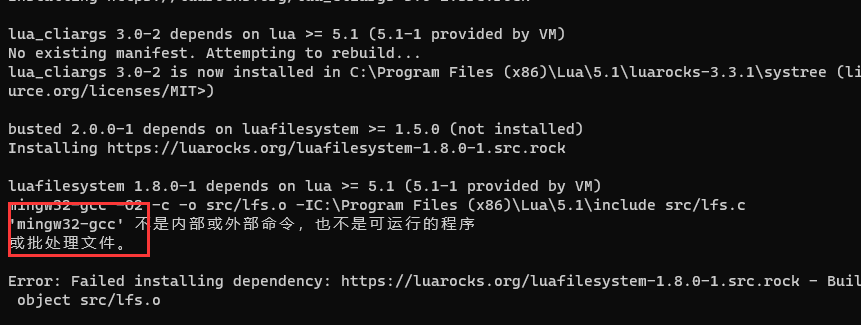
- 您需要安装gcc
- mingw下载安装(windows安装指南)
- 配置环境变量。 我的电脑->属性->高级系统设置->环境变量->系统变量
系统变量->Path->编辑->新建->D:\mingw\bin->确定
系统变量->新建->变量名:LIBRARY_path->变量值:D:\mingw\lib->确定
系统变量->新建->变量名:C_INCLUDE_PATH->变量值:D:\mingw\include->确定 - gcc -v验证安装
- 如若出现
安装其他库
安装busted
luarocks install busted 100%安装失败
使用别的方式安装
- 先安装
luarocks install luasocket安装成功后 再安装 busted luarocks install busted
安装 rapidjson
luarocks install rapidjson
安装 Lrexlib-PCRE2
luarocks install Lrexlib-PCRE2
出现错误
Could not find header file for PCRE2
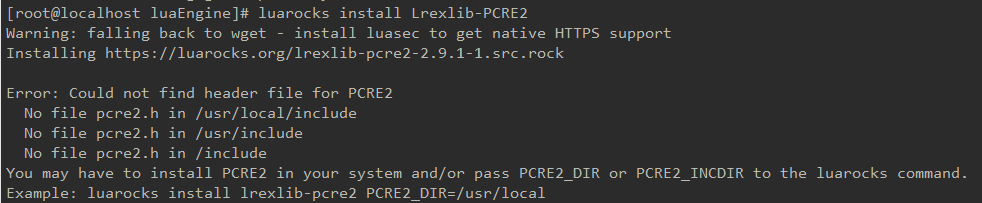
安装 pcre2yum -y install pcre2-devel
应该安装so库 yum -y install pcre2-static
find / -name "*pcre2.so*"
#输出路径
/usr/local/lib/lua/5.1/rex_pcre2.so拷贝至lua目录
